Types of B-tree indexes(Cluster Indexes) in Oracle11g
B-Tree cluster indexes:
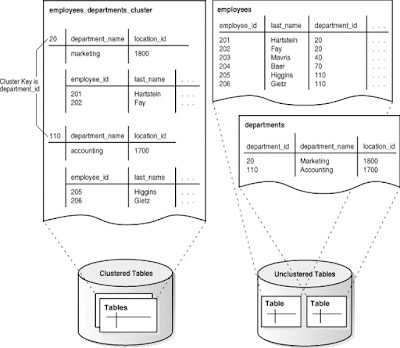
*This indexes(indexed cluster) is a table cluster that uses an index to locate data.
*The cluster index is a B-tree index on the cluster key ,It must be created before any rows can be instered into clustered tables
* A cluster is a group tables that share the same data blocks i.e all the tables are physically stored together
Create cluster:
Let us we can assume to create cluster based on the cluster key department_id
Then create index on it
Then create table emp and dept
*After inserting the rows the cluster table data will show like this example
To Dropping the cluster:
Note: This will drop the cluster ,if the cluster is empty which means no tables are existing it , otherwise we would drop the tables and then drop the cluster.
To Dropping the cluster with tables:
List the overall clusters:
Source: Oracle,Google,oracle-dba-online.com
*This indexes(indexed cluster) is a table cluster that uses an index to locate data.
*The cluster index is a B-tree index on the cluster key ,It must be created before any rows can be instered into clustered tables
* A cluster is a group tables that share the same data blocks i.e all the tables are physically stored together
Create cluster:
Let us we can assume to create cluster based on the cluster key department_id
SQL> create cluster emp_dept (department_id number(4));
Cluster created.
Then create index on it
SQL> create index idx_emp_dept on cluster emp_dept;
Index created.
Then create table emp and dept
SQL> create table emp (department_id number(4),
2 name varchar2(20),
3 empno number(5),
4 sal number(10,2))
5 cluster emp_dept (department_id);
Table created.
SQL> insert into emp values(10,'ram',123,'1500');
1 row created.
SQL> insert into emp values(20,'sam',124,'500');
1 row created.
SQL> insert into emp values(20,'dam',124,'600');
1 row created.
SQL> insert into emp values(30,'kam',125,'900');
1 row created.
SQL> insert into emp values(30,'tam',126,'1600');
1 row created.
SQL> commit;
Commit complete.
create table dept (department_id number(4),
name varchar2(20),
location varchar2(20))
cluster emp_dept (department_id);
SQL> insert into dept values (10,'ACCOUNTS','USA');
1 row created.
SQL> insert into dept values (20,'IT','SA');
1 row created.
SQL> insert into dept values (30,'SALES','KL');
1 row created.
SQL> commit;
Commit complete.
*After inserting the rows the cluster table data will show like this example

To Dropping the cluster:
SQL> Drop cluster emp_dept;
Note: This will drop the cluster ,if the cluster is empty which means no tables are existing it , otherwise we would drop the tables and then drop the cluster.
To Dropping the cluster with tables:
SQL>Drop cluster emp_dept including tables;
List the overall clusters:
SQL>select * from user_clusters;
To views which tables are part to the clusters:
SQL> select * from tab;
TNAME TABTYPE CLUSTERID
------------ ------- ----------
AF_TES TABLE
ARROW TABLE
ARROW_5 TABLE
COUNTRIES TABLE
DEPARTMENTS TABLE
DEPT TABLE 2
EMP TABLE 1
EMPLOYEES TABLE
EMP_DEPT CLUSTER
in above emp and dept tables are part of the cluster (Emp_dept). Source: Oracle,Google,oracle-dba-online.com
