High availability and scalability in oracle RAC 11g
High availability and scalability:
* As a dba most scraiest word or scariest area is down time we need to expertise in this particular ares.
*in that down time is the test to dba capcity only we can resolve by expertise and practice comes into picture at that time we can't google how do fail over and switch over?
reason of downtime::
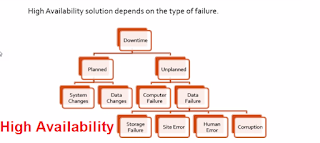
*as planned down time for os level paramter or the server team doing migaration old into new hardware
Planned Down time
*Its for doing hardware or software level ex: applying patches ,Server Hardware Upgrade,Server maintenance.
Unplanned downtime:
* 1)computer failure - our server completely blast,before the computer failure data failures causes the downtime.
Types of downtime::
*storage failure- let us take harddisk is data stored its totally gone
*site failure - due to some natural disaster our production server is gone
*Human error - someone deleting the data from database
*corruption - one block or sector are corrupted in hard disk
as a dba we have to take care our database from unplanned downtime
solution for downtime:
*Data corruption - Rman Backup
*Human error - Oracle Flashback
*site error - Oracle DataGuard
*storage Failure - oracle Asm
*computer Failure - Oracle Real application Cluster
with this downtime solution provided by oracle to achieve the high availability
what is MAA?
*the MAA stands for maximum availability architecture
*the environment which have the solution given below Rman,DataGuard,Flashback,OracleAsm,Oracle Rac
For more references:
Vertical Scalability:
*Increase the hardware capacity
*The existing hardware can't able to use
*adding the resource on hardware level
*It had a limitation on RAM,CPU and HDD
*This apporach is known as scale up
*Requires less management
Horizontal scalability:
*adding new resource with existing hardware
*this approach is known as scale out
*Requires cluster management software
*The processing power will be increase
*its limited by clusterware software not in the hardware that we use
combaining HS & VS:
*Real world combines with VS & HS
*start with a very high capacity server
*Low processor,RAM & HDD
*add processor ,RAM &HDD until server capacity is reached
*scale out by adding server by implementing cluster management software
Whatis Clusterware and grid?
*In oracle 9i it reduces the issue and released the name of "CRS"
*in oracle 10g the oracle released first own Clusterware software so the compatibility issues also solved and the Clusterware software name is "Grid".
Pre-requisites:
*Working Knowledge on Linux/Unix
*Basic Understanding Of networks
*Good at oracle DBA 10g or 11g
*Minimal Knowledge of Vmware or VirtualBox
* As a dba most scraiest word or scariest area is down time we need to expertise in this particular ares.
*in that down time is the test to dba capcity only we can resolve by expertise and practice comes into picture at that time we can't google how do fail over and switch over?
reason of downtime::

*as planned down time for os level paramter or the server team doing migaration old into new hardware
Planned Down time
*Its for doing hardware or software level ex: applying patches ,Server Hardware Upgrade,Server maintenance.
Unplanned downtime:
* 1)computer failure - our server completely blast,before the computer failure data failures causes the downtime.
Types of downtime::
*storage failure- let us take harddisk is data stored its totally gone
*site failure - due to some natural disaster our production server is gone
*Human error - someone deleting the data from database
*corruption - one block or sector are corrupted in hard disk
as a dba we have to take care our database from unplanned downtime
solution for downtime:
*Data corruption - Rman Backup
*Human error - Oracle Flashback
*site error - Oracle DataGuard
*storage Failure - oracle Asm
*computer Failure - Oracle Real application Cluster
with this downtime solution provided by oracle to achieve the high availability
what is MAA?
*the MAA stands for maximum availability architecture
*the environment which have the solution given below Rman,DataGuard,Flashback,OracleAsm,Oracle Rac
For more references:
Vertical Scalability:
*Increase the hardware capacity
*The existing hardware can't able to use
*adding the resource on hardware level
*It had a limitation on RAM,CPU and HDD
*This apporach is known as scale up
*Requires less management
Horizontal scalability:
*adding new resource with existing hardware
*this approach is known as scale out
*Requires cluster management software
*The processing power will be increase
*its limited by clusterware software not in the hardware that we use
combaining HS & VS:
*Real world combines with VS & HS
*start with a very high capacity server
*Low processor,RAM & HDD
*add processor ,RAM &HDD until server capacity is reached
*scale out by adding server by implementing cluster management software
Whatis Clusterware and grid?
*In oracle 9i it reduces the issue and released the name of "CRS"
*in oracle 10g the oracle released first own Clusterware software so the compatibility issues also solved and the Clusterware software name is "Grid".
Pre-requisites:
*Working Knowledge on Linux/Unix
*Basic Understanding Of networks
*Good at oracle DBA 10g or 11g
*Minimal Knowledge of Vmware or VirtualBox
